UH4L5——调用ILRuntime中方法
UH4L5——调用ILRuntime中方法
本章代码关键字
1 | appDomain.Invoke() //除了传入IMethod,对于方法直接传入类名,方法名,要执行方法的对象(静态方法不传入),参数,即可执行方法 |
跨域调用方法
-
静态方法
静态方法调用的规则和成员属性方法调用规则基本类似,三板斧调用:
-
appdomain.Invoke("命名空间.类名", "静态方法名", null, 参数列表) -
appdomain.Invoke(IMethod对象, null, 参数列表) - 无GC Alloc方式:
using(BeginInvoke){ push Invoke read -> ubpir }方式
注意:建议大家都使用类似反射的
IMethod来调用方法,并且使用更节约性能的无GC Alloc方式来调用 -
-
成员方法
三板斧调用(和静态方法调用区别就是,需要指明调用方法的对象)
-
appdomain.Invoke("命名空间.类名", "静态方法名", 对象, 参数列表) -
appdomain.Invoke(IMethod对象, 对象, 参数列表) - 无GC Alloc方式:
using(BeginInvoke){ push Invoke read -> ubpir }方式
-
-
重载方法
- 方法调用,还是遵循三板斧调用规则
- 参数数量不同时,通过明确参数数量来明确重载,参数数量相同,类型不同时,通过指明参数类型来明确重载
-
ref /out方法-
ref /out 方法只能通过无GC Alloc方法调用using(BeginInvoke){ push Invoke read -> ubpir }方式 -
在调用时多了三个步骤
- 需要先压入
ref或out参数的初始值 - 压入参数环节压入引用索引值
- 通过
Read 按顺序获取ref、out参数,返回值最后获取
- 需要先压入
-
静态方法调用
假设要调用热更新工程内的如下的静态方法(热更工程内可以直接调用UnityEngine命名空间内的内容):
1 | using UnityEngine; |
静态方法调用有两种方式
-
直接通过
appDomain.Invoke("命名空间.类名", "静态方法名", null, 参数列表),调用静方法这里是不传入
IMethod的重载,参数如下:- 参数一:
"命名空间.类名" - 参数二:方法名
- 参数三:要执行方法的对象,如果是静态方法则不填
- 后续参数:参数列表
该方法除了静态方法,还可以调用:成员方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12void Start()
{
ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.StartILRuntime(() =>
{
AppDomain appDomain = ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.appDomain;
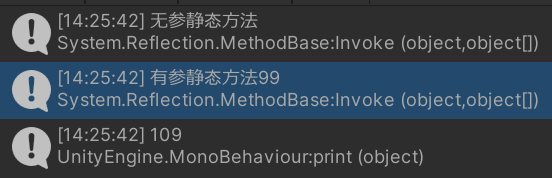
//无参方法调用
appDomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test", "TestStaticFun", null, null);
//有参有返回值调用
int i = (int)appDomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test", "TestStaticFun", null, 99);
print(i);
});
}输出:
- 参数一:
-
通过类似反射的
IMethod调用静态方法通过
IType中的GetMethod方法,类似反射一样的获取对应类中的静态方法1
2
3
4
5
6AppDomain appDomain = ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.appDomain;
IType type = appDomain.LoadedTypes["HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test"];
//无参无返回值
IMethod method1 = type.GetMethod("TestStaticFun", 0);
//有参有返回值
IMethod method2 = type.GetMethod("TestStaticFun2", 1);-
通过
appDomain.Invoke(方法名,null,参数)调用 静态方法1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15void Start()
{
ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.StartILRuntime(() =>
{
AppDomain appDomain = ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.appDomain;
IType type = appDomain.LoadedTypes["HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test"];
IMethod method1 = type.GetMethod("TestStaticFun", 0);
IMethod method2 = type.GetMethod("TestStaticFun2", 1);
//无参无返回值
appDomain.Invoke(method1, null, null);
//有参有返回值
int i2 = (int)appDomain.Invoke(method2, null, 88);
print(i2);
});
}输出:

-
通过更节约性能的无GC Alloc方式(调用完后直接回收)调用静态方法,类似上节课的成员属性
1
2
3
4
5
6using (var method = appDomain.BeginInvoke(methodName))
{
method.Push.....(1000);//传入指定类型参数
method.Invoke(); //执行方法
method.Read....() //获取指定类型返回值
}使用示例:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24void Start()
{
ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.StartILRuntime(() =>
{
AppDomain appDomain = ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.appDomain;
IType type = appDomain.LoadedTypes["HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test"];
IMethod method1 = type.GetMethod("TestStaticFun", 0);
IMethod method2 = type.GetMethod("TestStaticFun2", 1);
using (var method = appDomain.BeginInvoke(method1))
{
method.Invoke();
}
using (var method = appDomain.BeginInvoke(method2))
{
method.PushInteger(77);
method.Invoke();
int i3 = method.ReadInteger();
print(i3);
}
});
}输出:

-
成员方法调用
假设要调用热更新工程内的如下的成员方法(热更工程内可以直接调用UnityEngine命名空间内的内容):
1 | using UnityEngine; |
成员方法调用和静态方法调用几乎一样,区别就是需要先创建对象,将对象传入之前为null的地方
-
直接通过
appDomain.Invoke("命名空间.类名", "方法名", 类对象, 参数列表)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13void Start()
{
ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.StartILRuntime(() =>
{
AppDomain appDomain = ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.appDomain;
IType type = appDomain.LoadedTypes["HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test"];
object obj = ((ILType)type).Instantiate();
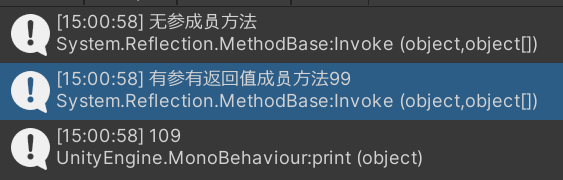
appDomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test", "TestFun", obj, null);
int i = (int)appDomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test", "TestFun2", obj, 99);
print(i);
});
}输出:
-
通过类似反射的
IMethod调用成员方法通过
IType中的GetMethod方法,类似反射一样的获取对应类中的方法1
2
3
4AppDomain appDomain = ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.appDomain;
IType type = appDomain.LoadedTypes["HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test"];
IMethod method1 = type.GetMethod("TestFun", 0);
IMethod method2 = type.GetMethod("TestFun2", 1);-
通过
appDomain.Invoke(IMethod对象, 类对象, 参数列表)调用 成员方法1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14void Start()
{
ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.StartILRuntime(() =>
{
AppDomain appDomain = ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.appDomain;
IType type = appDomain.LoadedTypes["HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test"];
IMethod method1 = type.GetMethod("TestFun", 0);
IMethod method2 = type.GetMethod("TestFun2", 1);
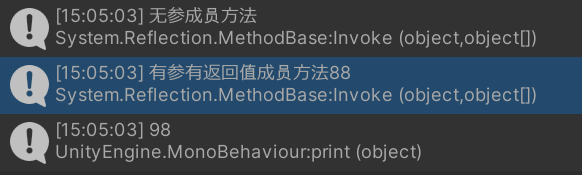
appDomain.Invoke(method1, obj);
int i2 = (int)appDomain.Invoke(method2, obj, 88);
print(i2);
});
}输出:
-
通过更节约性能的GC Alloc方式(调用完后直接回收)调用 成员方法,类似上节课的成员属性
调用成员方法,我们必须调用
InvocationContext.PushObject()来压入要执行方法的对象1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25void Start()
{
ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.StartILRuntime(() =>
{
AppDomain appDomain = ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.appDomain;
IType type = appDomain.LoadedTypes["HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test"];
IMethod method1 = type.GetMethod("TestFun", 0);
IMethod method2 = type.GetMethod("TestFun2", 1);
using (var method = appDomain.BeginInvoke(method1))
{
method.PushObject(obj);
method.Invoke();
}
using (var method = appDomain.BeginInvoke(method2))
{
method.PushObject(obj);
method.PushInteger(77);
method.Invoke();
int i3 = method.ReadInteger();
print(i3);
}
});
}输出:

-
重载方法调用
假设要调用热更新工程内的如下的重载方法(热更工程内可以直接调用UnityEngine命名空间内的内容):
1 | using UnityEngine; |
-
参数数量不同
-
通过
appDomain.Invoke调用参数数量不同的重载方法时,传入不同数量的参数即可自动分别调用不同参数1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12void Start()
{
ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.StartILRuntime(() =>
{
AppDomain appDomain = ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.appDomain;
IType type = appDomain.LoadedTypes["HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test"];
object obj = ((ILType)type).Instantiate();
appDomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test", "TestFun", obj);
appDomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test", "TestFun", obj, 1);
});
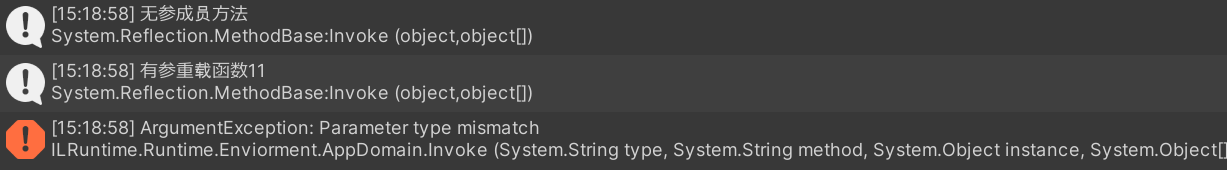
}但当存在数量相同而参数类型不同的重载时,就会因为无法明确调用哪种重载而报错
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13void Start()
{
ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.StartILRuntime(() =>
{
AppDomain appDomain = ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.appDomain;
IType type = appDomain.LoadedTypes["HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test"];
object obj = ((ILType)type).Instantiate();
appDomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test", "TestFun", obj);
appDomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test", "TestFun", obj, 1);
appDomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test", "TestFun", obj, 1.1f);
});
}输出:
-
通过
GetMethod的第二个参数来获取对应参数个数的函数1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28void Start()
{
ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.StartILRuntime(() =>
{
AppDomain appDomain = ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.appDomain;
IType type = appDomain.LoadedTypes["HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test"];
object obj = ((ILType)type).Instantiate();
appDomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test", "TestFun", obj);
appDomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test", "TestFun", obj, 1);
IMethod method1 = type.GetMethod("TestFun", 0);
IMethod method2 = type.GetMethod("TestFun", 1);
using (var method = appDomain.BeginInvoke(method1))
{
method.PushObject(obj);
method.Invoke();
}
using (var method = appDomain.BeginInvoke(method2))
{
method.PushObject(obj);
method.PushInteger(1);
method.Invoke();
}
});
}但同样的,当存在数量相同而参数类型不同的重载时,就会因为无法明确调用哪种重载而报错
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38void Start()
{
ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.StartILRuntime(() =>
{
AppDomain appDomain = ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.appDomain;
IType type = appDomain.LoadedTypes["HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test"];
object obj = ((ILType)type).Instantiate();
appDomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test", "TestFun", obj);
appDomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test", "TestFun", obj, 1);
//appDomain.Invoke("HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test", "TestFun", obj, 1.1f);
IMethod method1 = type.GetMethod("TestFun", 0);
IMethod method2 = type.GetMethod("TestFun", 1);
IMethod method3 = type.GetMethod("TestFun", 1);
using (var method = appDomain.BeginInvoke(method1))
{
method.PushObject(obj);
method.Invoke();
}
using (var method = appDomain.BeginInvoke(method2))
{
method.PushObject(obj);
method.PushInteger(1);
method.Invoke();
}
using (var method = appDomain.BeginInvoke(method3))
{
method.PushObject(obj);
method.PushInteger(1.1f);
method.Invoke();
}
});
}输出:

-
-
参数数量相同,类型不同,通过上面两种方式直接使用无法确定取出来的函数哪种重载,我们需要通过
GetMethod方法来获取指定参数类型的函数-
获取参数对应的
IType类型,利用appDomain中的GetType方法 获取指定变量类型的IType1
IType floatType = appDomain.GetType(typeof(float));
-
放入参数列表中,将获取到的
IType放入List<IType>中1
2List<IType> paramslist = new List<IType>();
paramslist.Add(floatType); -
传入
GetMethod中获取指定类型参数,使用GetMethod的另一个重载,传入指定类型获取方法信息1
IMethod method3 = type.GetMethod("TestFun", paramslist, null);
使用示例:
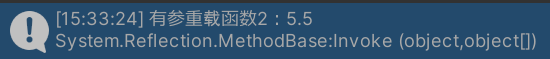
假设明确要调用参数列表为
float的重载方法1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21void Start()
{
ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.StartILRuntime(() =>
{
AppDomain appDomain = ILRuntimeMgr.Instance.appDomain;
IType type = appDomain.LoadedTypes["HotFix_Project.Lesson3_Test"];
object obj = ((ILType)type).Instantiate();
//明确要获取参数列表为float的重载
IType floatType = appDomain.GetType(typeof(float));
List<IType> paramslist = new List<IType>();
paramslist.Add(floatType);
IMethod method3 = type.GetMethod("TestFun", paramslist, null);
using (var method = appDomain.BeginInvoke(method3))
{
method.PushObject(obj);
method.PushFloat(5.5f);
method.Invoke();
}
});
}输出:
-
ref / out 方法调用
假设要调用热更新工程内的如下的重载方法(热更工程内可以直接调用UnityEngine命名空间内的内容):
1 | using System.Collections.Generic; |
需要通过IMethod方法调用,并且只能使用无GC Alloc方法调用
-
和其他函数不一样的地方,需要先压入
ref或out参数的初始值1
2
3
4
5
6
7using (var method = appDomain.BeginInvoke(methodInfo))
{
//压入第一个ref参数的初始值
method.PushObject(list);
//压入第一个out参数的初始值,由于out参数不需要在外部初始化 所以压入null即可
method.PushObject(null);
} -
和其它函数调用写法一致,压入调用对象,压入各参数
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12using (var method = appDomain.BeginInvoke(methodInfo))
{
//压入第一个ref参数的初始值
method.PushObject(list);
//压入第一个out参数的初始值,由于out参数不需要在外部初始化 所以压入null即可
method.PushObject(null);
//其他函数调用写法一致。压入调用对象
method.PushObject(obj);
//压入各参数
method.PushInteger(100);
} -
ref 和out 因为在一开始就压入了值,在这里需要压入他们的索引位置,后续需要通过传入的索引位置来获取值
ref 和out 参数 压入参数引用索引值即可 从0开始1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20using (var method = appDomain.BeginInvoke(methodInfo))
{
//压入第一个ref参数的初始值
method.PushObject(list);
//压入第一个out参数的初始值,由于out参数不需要在外部初始化 所以压入null即可
method.PushObject(null);
//其他函数调用写法一致
//压入调用对象
method.PushObject(obj);
//压入各参数
method.PushInteger(100);
//ref和out因为在一开始就压入的值,因此在这里需要压入参数引用的索引值,从0开始即可
//这里有两个ref和out参数,因此执行两次该方法即可
method.PushReference(0);
method.PushReference(1);
//执行方法
method.Invoke();
} -
通过
Read 按顺序获取ref /out 参数的值 和返回值,返回值最后获取
ref 和out 参数的获取需要传入索引值,索引值和PushReference传入的索引值对应1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25using (var method = appDomain.BeginInvoke(methodInfo))
{
//压入第一个ref参数的初始值
method.PushObject(list);
//压入第一个out参数的初始值,由于out参数不需要在外部初始化 所以压入null即可
method.PushObject(null);
//其他函数调用写法一致
//压入调用对象
method.PushObject(obj);
//压入各参数
method.PushInteger(100);
//ref和out因为在一开始就压入的值,因此在这里需要压入参数引用的索引值,从0开始即可
//这里有两个ref和out参数,因此执行两次该方法即可
method.PushReference(0);
method.PushReference(1);
//执行方法
method.Invoke();
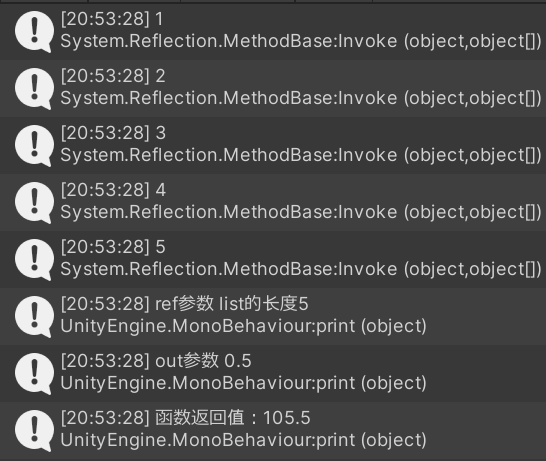
//通过Read按顺序获取ref/out参数的值 和返回值,返回值最后获取
list = method.ReadObject<List<int>>(0); //这里传入的索引值与PushReference传入的索引值对应
float f = method.ReadFloat(1); //这里传入的索引值与PushReference传入的索引值对应
float returnValue = method.ReadFloat(); //获取返回值,不需要传入索引
}
使用示例:
1 | void Start() |
输出: